How to prevent postpartum pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism (refers to the pathological and clinical state caused by the impacted material entering the pulmonary artery and its branches, blocking the blood supply to the tissue. There are various emboli that cause pulmonary embolism, including thrombus, fat, amniotic fluid, air or tumor emboli, etc. The clinical manifestations of pulmonary embolism are various, all lack specificity, and are easily overlooked or misdiagnosed. The severity of pulmonary embolism varies greatly, ranging from mild asymptomatic to severe hemodynamic instability or even sudden death. Although it is dangerous and has an acute onset, if correct identification and prevention can be done, this disease can be completely avoided!
1. What is pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities are both venous thromboembolism (referred to as VTE below). Pulmonary embolism is when a blood clot breaks off the lower extremities and travels to the lungs, causing one or more blood vessels to become blocked, resulting in a pulmonary embolism. The risk of pulmonary embolism during pregnancy and postpartum is higher than in non-pregnant women. Therefore, pregnant women especially need to be vigilant and prevent the occurrence of postpartum pulmonary embolism.
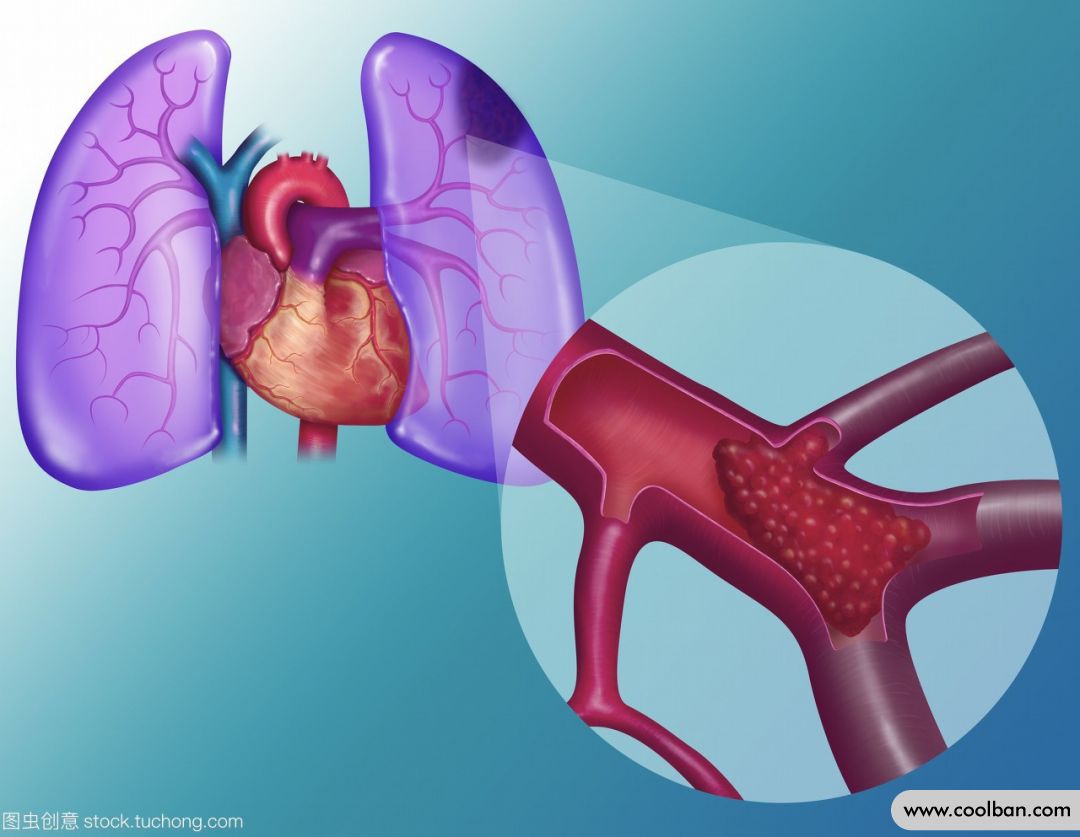
2. What are the symptoms of postpartum and need to suspect pulmonary embolism?
Postpartum symptoms such as dyspnea, chest pain, body bruising, and hemoptysis should be alerted to the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. In addition, it can also be manifested as chest tightness, suffocation, and shortness of breath. In the case of acute massive pulmonary embolism, it can be manifested as shock, heart failure, and respiratory failure. The mild cases are only palpitation and palpitations, and the electrocardiogram shows arrhythmia.
In addition, before the occurrence of postpartum pulmonary embolism, there is usually deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremity. If symptoms such as lower extremity pain and swelling occur, it is necessary to limit activities, do not massage the affected limb, and seek medical treatment as soon as possible, so as to strangle the postpartum pulmonary embolism in the cradle.
How to prevent pulmonary embolism after childbirth?
1. For mothers, they should do the following in their daily life:
(1) Reasonable maternal diet;
(2) Regularly carry out exercise during pregnancy;
(3) Avoid postpartum dehydration;
(4) Avoid prolonged bed rest or immobilization of mothers after childbirth;
(5) Encourage early post-operative movement of puerperae;
(6) Identify risk factors and early symptoms of VTE.
2. The following physical methods can be used as the first choice for preventive measures, and can also be used as adjuvant therapy for drug therapy in high-risk groups:
(1) Dorsiflexion of the foot;
(2) Antithrombotic gradient compression stockings: suitable for pregnant and lying-in women who can move freely during prenatal or puerperium, or wear gradient compression stockings while receiving drug anticoagulation;
(3) Intermittent pneumatic compression device or plantar venous pump: suitable for pregnant women who are in bed for a long time and have high risk factors, especially for women after cesarean section, for women who are not suitable for wearing gradient compression stockings Consider using overnight.
3. Pregnant women with high risk factors during pregnancy and postpartum, rational application of low molecular weight heparin injection can effectively prevent the occurrence of pulmonary embolism.
4. Some suggestions
Although the risk of pulmonary embolism in pregnant women is increased compared with the general population, in general, it is still a small probability event with an incidence of less than 1/1000, and there is no need to fear it.
Secondly, if pulmonary embolism occurs, the onset is acute and the change is rapid, which is very dangerous. However, many hospitals now have dynamic assessment of high-risk factors for VTE disease. For high-risk patients, early intervention and prevention can greatly reduce the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. , the incidence of lower extremity venous thrombosis, to avoid the serious consequences.
Finally, I also put forward a pertinent suggestion. If conditions permit, encourage the majority of female friends to have children at the best reproductive age to reduce many dangers caused by advanced age.
