What is cervical dysplasia?
In our daily life, many women suffer from cervical diseases, among which the more common cervical diseases are cervical polyps and cervical hyperplasia, and these two diseases can cause lesions, especially cancer, so female friends must cause Sufficient attention should be paid to timely treatment once the diagnosis is made. If the disease cannot be controlled in time and suffer from cervical cancer, the hysterectomy must be performed.
What is cervical dysplasia?
It refers to the abnormal and atypical differentiation of part or most of the female cervical epithelial cells. Dysplasia, also known as dysplasia, is a kind of precancerous lesions. Under the continued action of certain factors, it changes from quantitative to qualitative changes over time, and turns into malignant tumors.
The main reason is the infection of human papillomavirus (HPV) and the activation of HPV virus. The average time from HPV infection to cervical cancer to dysplasia is about 10 years.
During this period, it is important for women to prevent cervical cancer through accurate diagnosis and treatment, early detection for HPV infection, timely detection of cervical abnormalities and treatment in the precancerous stage.

HPV is the main cause of female warts, condyloma acuminatum and cervical cancer, and is divided into low-risk group and high-risk group according to the degree of malignancy.
Among them, the representative low-risk groups HPV6 and HPV11 often cause lesions such as warts and gonorrhea, and the high-risk groups HPV16 and HPV18 are very easy to develop into cervical cancer and other malignant tumors.
Since HPV infection is common in women, what is more important is the level of HPV activation according to immune status.
The prevalence of HPV infection in women is 10-20%. About 80% of sexually experienced adult women have had at least one HPV infection, but 70-80% of women infected with HPV will develop symptoms of HPV infection and associated epithelial changes within 2 years, and only a minority of women will have persistent HPV infection or the development of cervical cancer
Most women with cervical dysplasia are asymptomatic. Symptoms such as increased vaginal discharge, abnormal vaginal bleeding, recurrent vaginitis, or painful intercourse bleeding may occur.
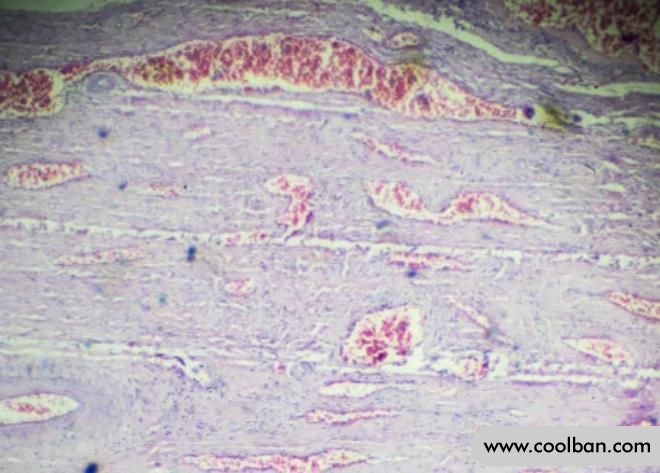
Cervical dysplasia progresses to stages 1, 2, and 3 with increasing degrees of cellular and tissue transformation.
In the case of stage 1, 60-80% of cases will disappear spontaneously, while in the case of stage 2 and 3, 5-10% chance of developing cancer. Periods of cervical dysplasia progress slowly over several years.
Women who have frequent vaginitis, increased discharge, or abdominal pain with irregular bleeding are advised to have an annual physical examination for HPV.
Because it is important to normalize the immune environment of the cervix, if the cervix is inflamed, immune-boosting therapy is recommended.
At each stage of cervical dysplasia, it is necessary to return to the previous stage to maintain a normal cervical state and prevent recurrence.
Most women with mild symptoms recover without treatment. Your doctor may recommend every 6 to 12 months instead of every 3 to 5 Have a Pap test every year. But if these changes don't go away or get worse, treatment is needed.

Women with moderate or severe cervical dysplasia may require immediate treatment.
The best way to prevent cervical dysplasia in women is to get the HPV vaccine. It has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of HPV infection in women.
