What are the dangers of uterine fibroids?
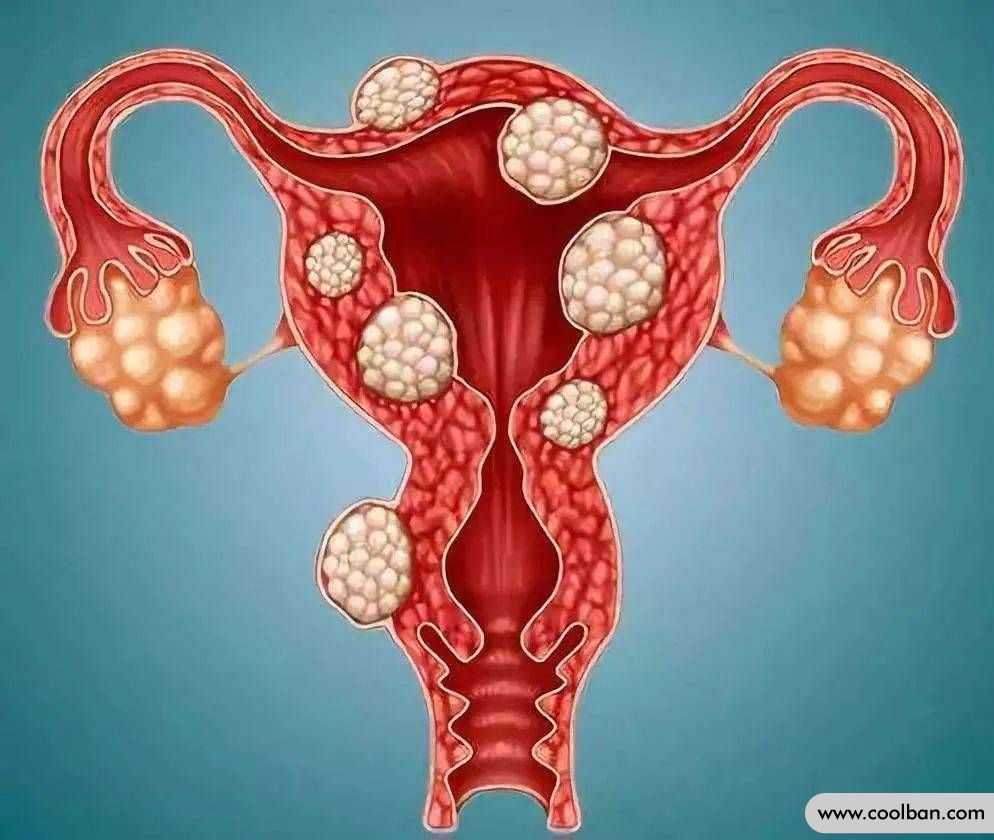
First, what is uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors formed by the hyperplasia of uterine smooth muscle. The incidence rate is as high as about 30%. It is more common in childbearing age, and the age of onset is between 30 and 50 years old. It is the most common tumor in women.
Uterine fibroids are mainly affected by the level of estrogen in women, and the common causes are the strong secretion of estrogen in women, cytokines, genetics and other factors, also known as estrogen-dependent tumors.
What harm does uterine fibroids bring to women?
Harm 1. Changes in menstruation, manifested as shortening of women's menstrual cycle, prolonged menstrual period, increased menstrual volume, irregular vaginal bleeding and other symptoms, endangering women's health.
Hazard two, abdominal distension, accompanied by a sense of falling.
Hazard 3. Increased leucorrhea, and rarely produces a large amount of pus and bloody discharge and slough-like tissue discharge with foul smell.
Hazard 4. There are often lower abdominal bulge and lower back pain. When the subserosal fibroid pedicle is reversed, acute abdominal pain can occur.
Hazard 5. When fibroids grow forward or backward, it can compress the urethra, bladder or rectum, causing frequent urination, urinary retention or constipation.
Hazard 6. Fibroids may compress the fallopian tube to distort it, or deform the uterine cavity so as to prevent the implantation of the fertilized egg, resulting in infertility. It will also cause the fertilized egg to fail to implant in the uterus because of too many fibroids, endangering the reproductive health of women.
Hazard 7. Long-term menorrhagia in female patients will lead to secondary anemia, and symptoms such as paleness, general weakness, shortness of breath, and palpitation will appear.
Will uterine fibroids become malignant?
Uterine fibroids may become cancerous, but the probability of canceration is very low, only about 0.5%. If the fibroids are multiple and small, and the growth rate is relatively slow, there is generally no need to worry, and regular inspections are sufficient.
If the fibroids grow rapidly and are accompanied by vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, etc., the possibility of malignant transformation cannot be ruled out, and timely examination and treatment are required. Postoperative pathological examination can determine whether malignant transformation.
Can uterine fibroids be eliminated by taking medicine?
Uterine fibroids cannot be eliminated by taking medicine, because the inside of fibroids is actually smooth muscle and connective tissue. Drugs can only reduce or reduce the growth rate of leiomyomas, but they cannot be eliminated.
Do uterine fibroids need surgery?
Usually, women with fibroids smaller than 5 cm do not require treatment if they do not cause increased menstrual flow, prolonged menstrual periods, or abdominal pain or discomfort.
Especially for menopausal women, because fibroids may shrink or disappear after menopause, as long as they are checked once every six months or a year.
How big does uterine fibroids need surgery?
The indications for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids are comprehensive. Whether or not surgery is required depends not only on the size of the fibroids, but also on whether the female patient has clinical symptoms, such as uterine menorrhagia, abnormal bleeding, abnormal urination and other oppressive symptoms.
For example, uterine fibroids located under the mucous membrane, even if they are small in size, will have relatively obvious abnormal bleeding, and even affect women's pregnancy, and can be treated by myomectomy. If the fibroids are located in the myometrium or subserosal, when the fibroids are small, the clinical symptoms are not obvious, and surgery is generally not required. If the fibroids grow to about 4-6 cm and cause obvious clinical symptoms, surgery can be considered.
