Monkeypox prevention and control knowledge
2022-06-08
In addition to the new crown epidemic, one of the hotspots related to infectious diseases that has recently attracted global attention is "monkeypox". This article will give a brief introduction to "monkeypox" based on the collected and collated data.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of May 20, 11 countries around the world have reported about 80 cases of human infection with monkeypox virus, and another 50 suspected cases of monkeypox are pending. This is a significant increase from the more than 50 cases in the four countries a few days ago. Among them, Europe is more affected, involving Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Confirmed cases have also been found in the United States, Canada, and Australia. The WHO said that as surveillance expanded, more cases could be detected.
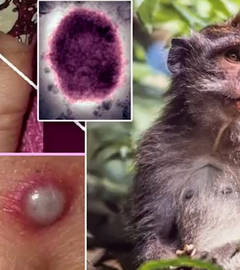
1. What is "monkeypox"? Is it related to the well-known "chicken pox" and "smallpox" ?
The first thing to understand here is that "monkeypox" and "chickenpox" are not close relatives! In terms of biological classification, the full name of chickenpox is "varicella-zoster virus", which belongs to the family Herpesviridae, and is close relative to herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, and EB virus; while monkeypox belongs to the family Poxviridae, which has been in the family for more than 40 years. The previously declared eradication of the smallpox virus is a close relative; they are both DNA viruses.
Second, the similarities and differences between smallpox virus and monkeypox virus?
Smallpox virus only infects humans; monkeypox is a zoonotic virus that exists not only in monkeys, but also in animals such as mice and squirrels, and is mainly transmitted to various wild animals such as rodents and primates. people, but human-to-human transmission can also take place among humans.
Because monkeypox is similar to smallpox, monkeypox infection in humans is characterized by fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes, followed by pus-filled blisters that resemble smallpox lesions. Monkeypox lesions go through the following stages before shedding: macules, papules, blisters, pustules, crusts. Monkeypox usually lasts 2-4 week. The incubation period for monkeypox is usually 7-14 days, but it can be 5-21 days.

3. Why does the monkeypox epidemic occur?
Some experts believe that the emergence of monkeypox may be related to the "elimination" of the smallpox virus in humans. Since the global eradication of smallpox, people have stopped vaccinating against smallpox virus, but this smallpox virus vaccine is also very effective against monkeypox, about 85% effective. On May 8, 1980, WHO announced the global eradication of smallpox and recommended that countries stop vaccinating against smallpox. It is equivalent to the population under the age of 45 in the world. Most of them have not been vaccinated against smallpox. People born after that naturally have no immunity against smallpox virus and monkeypox virus in their bodies (1977-1978 was the last vaccination against smallpox in my country), So this may have contributed to the increase in monkeypox cases.
On the other hand, monkeypox virus is not a new virus. It may exist in the world for centuries or even thousands of years. However, through mutation, its infectivity and pathogenicity are also increasing. When the virus has the opportunity to contact When it reaches the human body, it may cause disease.
4. How many kinds of monkeypox virus are there?
Like the new coronavirus, monkeypox virus has different variants. Two variants currently exist. West African strains are weak in pathogenicity, with a case fatality rate of only 1% The Central African strain has strong pathogenicity, and the fatality rate is almost 10%. At present, only the West African branch of the virus has been found in the UK, and virus sequencing information elsewhere is unknown.

5. How is monkeypox spread?
Mainly through contact transmission and droplet transmission. Monkeypox infection occurs through broken skin, mucous membranes, respiratory droplets, infected bodily fluids, and even contact with contaminated bed sheets. But human-to-human transmission occurs primarily through large respiratory droplets, and because such droplets typically travel only a few feet, prolonged face-to-face contact is required to become infected.

6. Is monkeypox virus highly infectious?
In previous studies, it was found that monkeypox is not very contagious, and it can even be said that it is difficult to spread from person to person. The basic reproduction number (R0) is considered to be only 0.6~1.0. R0 is the number of people an infectious disease patient can infect on average, R0 < 1 The disease will gradually disappear. So this also means that monkeypox will not be a pandemic like the new crown pneumonia (the new coronavirus Omicron R0 is around 7). The incidence of monkeypox is mainly transmitted from close contact with animals, rather than from humans to humans. In the past cases, there are few confirmed cases of human-to-human transmission.

7. What are the main clinical manifestations of monkeypox? Is there any special medicine?
People infected with monkeypox develop a large rash on the face and body, including the inside of the mouth, palms and soles of the feet. Pain-triggering pimples are pearly, fluid-filled bumps, often with a red circle of surrounding skin, and the lesions eventually crust over and heal within two to three weeks. Although the mortality rate of monkeypox infection is not high, the greatest harm to people may come from vision - the most obvious feature of this disease is the appearance of a very scary looking rash, which is basically unacceptable to people with hyperphobia The effect, once the disease will have a greater impact on the psychological. At present, there is no specific drug available for the treatment of monkeypox, so supportive treatment is the mainstay.
In addition, the World Health Organization says that children infected with monkeypox are more likely to develop severe disease than adults. Infections during pregnancy can also lead to complications, including stillbirth.

Eight, monkeypox resistance to disinfectants?
As of now, most monkeypox cases have been mild. Handwashing, along with other preventive measures implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic, is critical to reducing the spread of monkeypox in healthcare settings. According to information from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ordinary household disinfectants can effectively remove monkeypox virus from surfaces.
IX. Is there a vaccine to prevent monkeypox?
The smallpox vaccine Jynneos, developed by Denmark-based vaccine company Bavarian Nordic, won the U.S. FDA in 2018 Approved for marketing for the prevention of smallpox (smallpox) and monkeypox (monkeypox) infection in high-risk adults over 18 years of age. This is the FDA The only approved non-replicating smallpox vaccine and has received approval for the smallpox monkeypox vaccine in Europe and Canada. This is the only approved smallpox monkeypox vaccine in the world.
10. How to do a good job in protection?
1. Avoid contact with animals that may carry monkeypox virus (mainly primates, rodents, marsupials in southern Africa);
2. Avoid eating game, especially when traveling in southern Africa;
3. Avoid contact with any items that have been in contact with monkeypox patients, such as bedding;
4. Isolate monkeypox-infected patients from others who may be at risk of infection;
5. Maintain good hand hygiene after contact with monkeypox-infected animals or humans. For example, wash your hands with soap and water, or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer;
6. Use personal protective equipment when caring for monkeypox patients.

According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of May 20, 11 countries around the world have reported about 80 cases of human infection with monkeypox virus, and another 50 suspected cases of monkeypox are pending. This is a significant increase from the more than 50 cases in the four countries a few days ago. Among them, Europe is more affected, involving Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Confirmed cases have also been found in the United States, Canada, and Australia. The WHO said that as surveillance expanded, more cases could be detected.

1. What is "monkeypox"? Is it related to the well-known "chicken pox" and "smallpox" ?
The first thing to understand here is that "monkeypox" and "chickenpox" are not close relatives! In terms of biological classification, the full name of chickenpox is "varicella-zoster virus", which belongs to the family Herpesviridae, and is close relative to herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, and EB virus; while monkeypox belongs to the family Poxviridae, which has been in the family for more than 40 years. The previously declared eradication of the smallpox virus is a close relative; they are both DNA viruses.
Second, the similarities and differences between smallpox virus and monkeypox virus?
Smallpox virus only infects humans; monkeypox is a zoonotic virus that exists not only in monkeys, but also in animals such as mice and squirrels, and is mainly transmitted to various wild animals such as rodents and primates. people, but human-to-human transmission can also take place among humans.
Because monkeypox is similar to smallpox, monkeypox infection in humans is characterized by fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes, followed by pus-filled blisters that resemble smallpox lesions. Monkeypox lesions go through the following stages before shedding: macules, papules, blisters, pustules, crusts. Monkeypox usually lasts 2-4 week. The incubation period for monkeypox is usually 7-14 days, but it can be 5-21 days.

3. Why does the monkeypox epidemic occur?
Some experts believe that the emergence of monkeypox may be related to the "elimination" of the smallpox virus in humans. Since the global eradication of smallpox, people have stopped vaccinating against smallpox virus, but this smallpox virus vaccine is also very effective against monkeypox, about 85% effective. On May 8, 1980, WHO announced the global eradication of smallpox and recommended that countries stop vaccinating against smallpox. It is equivalent to the population under the age of 45 in the world. Most of them have not been vaccinated against smallpox. People born after that naturally have no immunity against smallpox virus and monkeypox virus in their bodies (1977-1978 was the last vaccination against smallpox in my country), So this may have contributed to the increase in monkeypox cases.
On the other hand, monkeypox virus is not a new virus. It may exist in the world for centuries or even thousands of years. However, through mutation, its infectivity and pathogenicity are also increasing. When the virus has the opportunity to contact When it reaches the human body, it may cause disease.
4. How many kinds of monkeypox virus are there?
Like the new coronavirus, monkeypox virus has different variants. Two variants currently exist. West African strains are weak in pathogenicity, with a case fatality rate of only 1% The Central African strain has strong pathogenicity, and the fatality rate is almost 10%. At present, only the West African branch of the virus has been found in the UK, and virus sequencing information elsewhere is unknown.

5. How is monkeypox spread?
Mainly through contact transmission and droplet transmission. Monkeypox infection occurs through broken skin, mucous membranes, respiratory droplets, infected bodily fluids, and even contact with contaminated bed sheets. But human-to-human transmission occurs primarily through large respiratory droplets, and because such droplets typically travel only a few feet, prolonged face-to-face contact is required to become infected.

6. Is monkeypox virus highly infectious?
In previous studies, it was found that monkeypox is not very contagious, and it can even be said that it is difficult to spread from person to person. The basic reproduction number (R0) is considered to be only 0.6~1.0. R0 is the number of people an infectious disease patient can infect on average, R0 < 1 The disease will gradually disappear. So this also means that monkeypox will not be a pandemic like the new crown pneumonia (the new coronavirus Omicron R0 is around 7). The incidence of monkeypox is mainly transmitted from close contact with animals, rather than from humans to humans. In the past cases, there are few confirmed cases of human-to-human transmission.

7. What are the main clinical manifestations of monkeypox? Is there any special medicine?
People infected with monkeypox develop a large rash on the face and body, including the inside of the mouth, palms and soles of the feet. Pain-triggering pimples are pearly, fluid-filled bumps, often with a red circle of surrounding skin, and the lesions eventually crust over and heal within two to three weeks. Although the mortality rate of monkeypox infection is not high, the greatest harm to people may come from vision - the most obvious feature of this disease is the appearance of a very scary looking rash, which is basically unacceptable to people with hyperphobia The effect, once the disease will have a greater impact on the psychological. At present, there is no specific drug available for the treatment of monkeypox, so supportive treatment is the mainstay.
In addition, the World Health Organization says that children infected with monkeypox are more likely to develop severe disease than adults. Infections during pregnancy can also lead to complications, including stillbirth.

Eight, monkeypox resistance to disinfectants?
As of now, most monkeypox cases have been mild. Handwashing, along with other preventive measures implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic, is critical to reducing the spread of monkeypox in healthcare settings. According to information from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ordinary household disinfectants can effectively remove monkeypox virus from surfaces.

IX. Is there a vaccine to prevent monkeypox?
The smallpox vaccine Jynneos, developed by Denmark-based vaccine company Bavarian Nordic, won the U.S. FDA in 2018 Approved for marketing for the prevention of smallpox (smallpox) and monkeypox (monkeypox) infection in high-risk adults over 18 years of age. This is the FDA The only approved non-replicating smallpox vaccine and has received approval for the smallpox monkeypox vaccine in Europe and Canada. This is the only approved smallpox monkeypox vaccine in the world.

10. How to do a good job in protection?
1. Avoid contact with animals that may carry monkeypox virus (mainly primates, rodents, marsupials in southern Africa);
2. Avoid eating game, especially when traveling in southern Africa;
3. Avoid contact with any items that have been in contact with monkeypox patients, such as bedding;
4. Isolate monkeypox-infected patients from others who may be at risk of infection;
5. Maintain good hand hygiene after contact with monkeypox-infected animals or humans. For example, wash your hands with soap and water, or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer;
6. Use personal protective equipment when caring for monkeypox patients.

