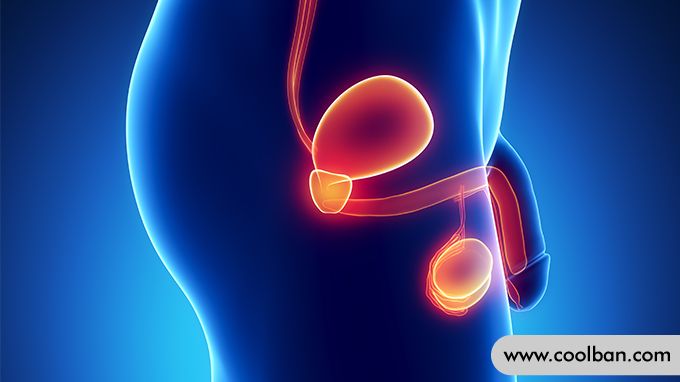
How to judge male prostate condition
Male prostate diseases mainly include prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostate cancer.
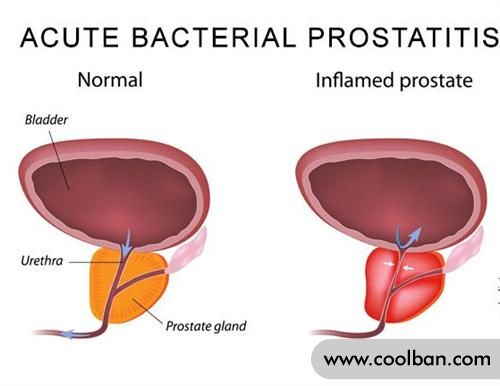
Male prostatitis, especially male chronic prostatitis, has become a difficult disease because of its complex and variable symptoms and no specificity. To sum up, in addition to a history of urethritis, urinary tract obstruction, and urinary tract infection, there are mainly the following five groups of symptoms. Through these 5 groups of symptoms, you can basically judge whether you have male prostatitis.
5 symptoms of prostatitis in men:
(1) Male urinary tract symptoms
A milky white discharge is common in the urethra, especially in cases of increased abdominal pressure such as defecation. The patient has frequent urination, urgency, dysuria, excess urination, burning sensation in the urethra during urination, and increased nocturia.
(2) Pain
The perineum, anus, and posterior urethra are the main areas where discomfort or pain occurs. In addition, the patient has discomfort or dull pain in the suprapubic, groin, lumbosacral, testis, penis, etc., or has varying degrees of reflexes below the thighs and above the knees. Sexual pain.
(3) Male reproductive system symptoms
Visible loss of libido, impotence, premature ejaculation, hematospermia, nocturnal emission and other sexual dysfunction and poor semen liquefaction, low sperm motility, decreased motility, abnormal sperm increase and semen agglutination and other phenomena.
(4) Male mental depression symptoms
The patients suffer from lack of energy, worry, irritability, insomnia, dreaminess, forgetfulness, etc., and even anxiety, fear, anger, low self-esteem, and even suicidal tendencies in severe cases.
(5) Other symptoms
The main symptoms of patients are fatigue, weak waist and knees, dizziness, tinnitus, constipation or looseness.
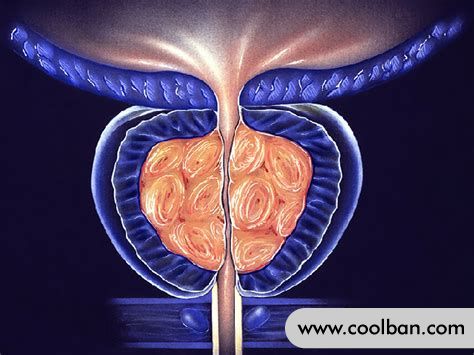
The main symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia are:
(1) Difficulty urinating
As the prostate disease continues to develop, each urination time is prolonged, the range is shorter, and the urine flow gradually becomes thin and weak. When prostate patients need to take a deep breath due to holding their urine for too long, the flow of urine is also interrupted with changes in abdominal pressure, and they must try again to make the urine continue to be discharged, so there is intermittent urination, and prostate patients always feel that the bladder is not discharged. Empty and inexhaustible feeling.
(2) Frequent urination
Men usually urinate 6 to 7 times during the day and 2 to 3 or 5 to 6 times at night. This is due to urethral obstruction caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. The urine in the bladder cannot be completely emptied each time urination. There is often residual urine in the bladder, and the effective capacity is reduced, so the urination interval is shortened, and frequent urination occurs. In addition, the mucosa of the bladder neck is often congested, and irritation of the bladder can also cause frequent urination. In the later stage, the patient urinates one or more times per hour, which seriously affects the patient's work and life, especially on the patient's sleep, causing the patient to feel physically and mentally exhausted.
(3) Urinary retention
After each urination, there is residual urine in the bladder, and as the urinary tract obstruction increases, the residual urine volume in the bladder increases. In 40% to 60% of patients, due to cold, drinking, fatigue and other factors, the prostate suddenly becomes congested and swollen, compressing the urethra, causing acute urinary retention, and suddenly unable to urinate. hours or even longer after a hospital visit. At this time, the male bladder has been extremely distended and very painful.
(4) Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence in men is a later symptom. When the urine in the bladder exceeds the resistance of the patient's urethral sphincter due to urinary retention, the bladder is over-inflated, and the urine is like a river that loses the control of the gate and continuously overflows from the urethra, which is called "pseudo-incontinence". Especially when men are asleep at night, it is more serious.